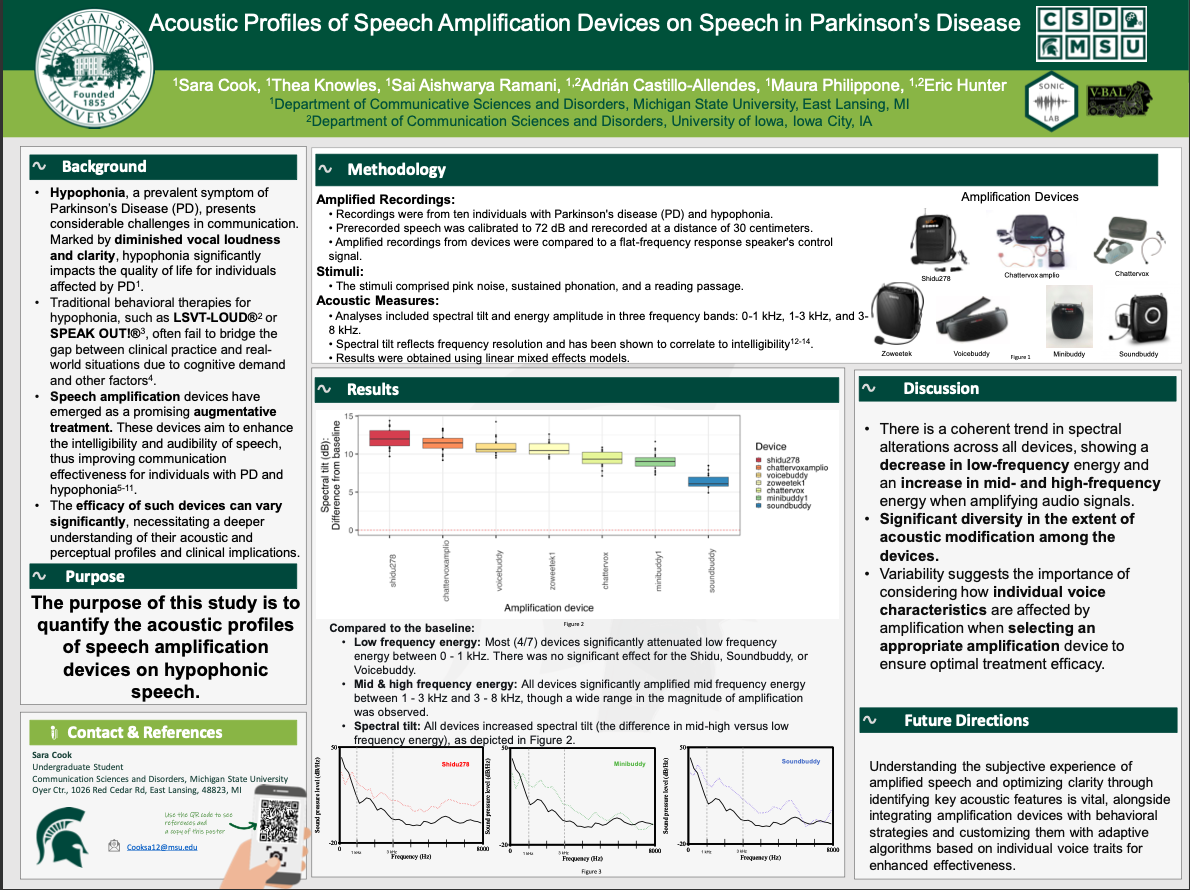
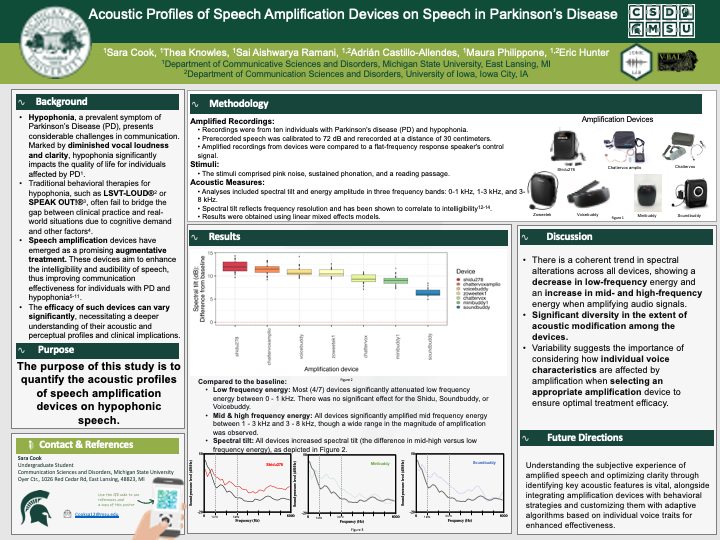
Acoustic Profiles of Speech Amplification Devices on Speech in Parkinson’s Disease
Sara Cook, Thea Knowles, Sai Aishwarya Ramani, Adrián Castillo-Allendes, Maura Philippone, Eric Hunter
Presented at the MSU 2024 University Undergraduate Research and Arts Forum (UURAF), Michigan Speech Language Hearing Association Conference , and the 2024 Voice Foundation Conference
East Lansing, Michigan April 12th, 2024
Muskegon, Michigan April 19th, 2024
May 30th, 2024
UURAF
Listen to some example audio
References
1 Adams, S.G. & Dykstra, A. (2009). Hypokinetic dysarthria. In M.R. McNeil (Ed.). Clinical management of sensorimotor speech disorders (pp. 166–186). New York, NY: Thieme Medical Publishers.
2 Andreetta, M. D., Adams, S. G., Dykstra, A. D., & Jog, M. (2016). Evaluation of Speech Amplification Devices in Parkinson’s Disease. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 25(1), 28–45. https://doi-org.proxy2.cl.msu.edu/10.1044/2015_AJSLP-15-0008
3 Bain, C., Ferguson, A., & Mathisen, B. (2005). Effectiveness of the Speech Enhancer on intelligibility: a case study. Journal of Medical Speech - Language Pathology, 13(2), 85.
4 Gaballah, A., Parsa, V., Andreetta, M., & Adams, S. (2019). Objective and Subjective Speech Quality Assessment of Amplification Devices for Patients With Parkinson’s Disease. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, IEEE Transactions on, IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng, 27(6), 1226–1235. https://doi-org.proxy2.cl.msu.edu/10.1109/TNSRE.2019.2915172
5 Greene, M. C. L., Watson, B. W., Gay, P., & Townsend, D. B. K. (1972). A therapeutic speech amplifier and its use in speech therapy. The Journal of Laryngology & Otology, 86(6), 595-605–605. https://doi-org.proxy2.cl.msu.edu/10.1017/S0022215100075629
6 Knowles, T., Adams, S. G., Page, A., Cushnie-Sparrow, D., & Jog, M. (2020). A Comparison of Speech Amplification and Personal Communication Devices for Hypophonia. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 63(8), 2695–2712. https://doi-org.proxy2.cl.msu.edu/10.1044/2020_JSLHR-20-00085
7 Iddon, H., Read, J., & Miller, N. (2015). Does voice amplification increase intelligibility in people with Parkinson’s disease? International Journal of Therapy & Rehabilitation, 22(10), 479–486. https://doi-org.proxy2.cl.msu.edu/10.12968/ijtr.2015.22.10.479
8 Neel AT. (2009). Effects of loud and amplified speech on sentence and word intelligibility in Parkinson disease. Journal of Speech, Language & Hearing Research, 52(4), 1021–1033. https://doi-org.proxy2.cl.msu.edu/10.1044/1092-4388(2008/08-0119)
9 Badh G, Knowles T. Acoustic and perceptual impact of face masks on speech: A scoping review. PLoS One. 2023 Aug 25;18(8):e0285009. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0285009. PMID: 37624795; PMCID: PMC10456191
10 Cline, N., Knowles, T., & Badh, G. (2023). Effect of Face Masks and Speech Style on Speech Intelligibility and Listener Effort in Parkinson’s Disease. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 32(5), 2282–2296. https://doi-org.proxy1.cl.msu.edu/10.1044/2023_AJSLP-23-00085
11 Simantiraki, O., Cooke, M., & Pantazis, Y. (2020). Effects of Spectral Tilt on Listeners’ Preferences And Intelligibility. ICASSP 2020 - 2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), ICASSP 2020 - 2020 IEEE International Conference On, 6254–6258. https://doi-org.proxy2.cl.msu.edu/10.1109/ICASSP40776.2020.905411
MSHA
Listen to some audio
References
1 Adams, S.G. & Dykstra, A. (2009). Hypokinetic dysarthria. In M.R. McNeil (Ed.). Clinical management of sensorimotor speech disorders (pp. 166–186). New York, NY: Thieme Medical Publishers.
2 Behrman, A., Cody, J., Elandary, S., Flom, P., & Chitnis, S. (2020). The effect of SPEAK OUT! And the LOUD Crowd on dysarthria due to Parkinson’s disease. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 1–18.
3 Yuan, F., Guo, X., Wei, X., Xie, F., Zheng, J., Huang, Y., Huang, Z., Chang, Z., Li, H., Guo, Y., Chen, J., Guo, J., Tang, B., Deng, B., & Wang, Q. (2020). Lee Silverman Voice Treatment for dysarthria in patients with Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. European Journal of Neurology, 27(10), 1957–1970. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.14399
4 Yorkston, K., Baylor, C., & Britton, D. (2017). Speech Versus Speaking: The Experiences of People With Parkinson’s Disease and Implications for Intervention. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 26(2S), 561–568. https://doi-org.proxy2.cl.msu.edu/10.1044/2017_AJSLP-16-0087
5 Andreetta, M. D., Adams, S. G., Dykstra, A. D., & Jog, M. (2016). Evaluation of Speech Amplification Devices in Parkinson’s Disease. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 25(1), 28–45. https://doi-org.proxy2.cl.msu.edu/10.1044/2015_AJSLP-15-0008
6 Bain, C., Ferguson, A., & Mathisen, B. (2005). Effectiveness of the Speech Enhancer on intelligibility: a case study. Journal of Medical Speech - Language Pathology, 13(2), 85.
7 Gaballah, A., Parsa, V., Andreetta, M., & Adams, S. (2019). Objective and Subjective Speech Quality Assessment of Amplification Devices for Patients With Parkinson’s Disease. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, IEEE Transactions on, IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng, 27(6), 1226–1235. https://doi-org.proxy2.cl.msu.edu/10.1109/TNSRE.2019.2915172
8 Greene, M. C. L., Watson, B. W., Gay, P., & Townsend, D. B. K. (1972). A therapeutic speech amplifier and its use in speech therapy. The Journal of Laryngology & Otology, 86(6), 595-605–605. https://doi-org.proxy2.cl.msu.edu/10.1017/S0022215100075629
9 Knowles, T., Adams, S. G., Page, A., Cushnie-Sparrow, D., & Jog, M. (2020). A Comparison of Speech Amplification and Personal Communication Devices for Hypophonia. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 63(8), 2695–2712. https://doi-org.proxy2.cl.msu.edu/10.1044/2020_JSLHR-20-00085
10 Iddon, H., Read, J., & Miller, N. (2015). Does voice amplification increase intelligibility in people with Parkinson’s disease? International Journal of Therapy & Rehabilitation, 22(10), 479–486. https://doi-org.proxy2.cl.msu.edu/10.12968/ijtr.2015.22.10.479
11 Neel AT. (2009). Effects of loud and amplified speech on sentence and word intelligibility in Parkinson disease. Journal of Speech, Language & Hearing Research, 52(4), 1021–1033. https://doi-org.proxy2.cl.msu.edu/10.1044/1092-4388(2008/08-0119)
12 Badh G, Knowles T. Acoustic and perceptual impact of face masks on speech: A scoping review. PLoS One. 2023 Aug 25;18(8):e0285009. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0285009. PMID: 37624795; PMCID: PMC10456191
13 Cline, N., Knowles, T., & Badh, G. (2023). Effect of Face Masks and Speech Style on Speech Intelligibility and Listener Effort in Parkinson’s Disease. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 32(5), 2282–2296. https://doi-org.proxy1.cl.msu.edu/10.1044/2023_AJSLP-23-00085
14 Simantiraki, O., Cooke, M., & Pantazis, Y. (2020). Effects of Spectral Tilt on Listeners’ Preferences And Intelligibility. ICASSP 2020 - 2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), ICASSP 2020 - 2020 IEEE International Conference On, 6254–6258. https://doi-org.proxy2.cl.msu.edu/10.1109/ICASSP40776.2020.905411
Voice Foundation
Listen to some audio
Resources
1 Adams, S.G. & Dykstra, A. (2009). Hypokinetic dysarthria. In M.R. McNeil (Ed.). Clinical management of sensorimotor speech disorders (pp. 166–186). New York, NY: Thieme Medical Publishers.
2 Behrman, A., Cody, J., Elandary, S., Flom, P., & Chitnis, S. (2020). The effect of SPEAK OUT! And the LOUD Crowd on dysarthria due to Parkinson’s disease. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 1–18.
3 Yuan, F., Guo, X., Wei, X., Xie, F., Zheng, J., Huang, Y., Huang, Z., Chang, Z., Li, H., Guo, Y., Chen, J., Guo, J., Tang, B., Deng, B., & Wang, Q. (2020). Lee Silverman Voice Treatment for dysarthria in patients with Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. European Journal of Neurology, 27(10), 1957–1970. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.14399
4 Yorkston, K., Baylor, C., & Britton, D. (2017). Speech Versus Speaking: The Experiences of People With Parkinson’s Disease and Implications for Intervention. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 26(2S), 561–568. https://doi-org.proxy2.cl.msu.edu/10.1044/2017_AJSLP-16-0087
5 Andreetta, M. D., Adams, S. G., Dykstra, A. D., & Jog, M. (2016). Evaluation of Speech Amplification Devices in Parkinson’s Disease. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 25(1), 28–45. https://doi-org.proxy2.cl.msu.edu/10.1044/2015_AJSLP-15-0008
6 Bain, C., Ferguson, A., & Mathisen, B. (2005). Effectiveness of the Speech Enhancer on intelligibility: a case study. Journal of Medical Speech - Language Pathology, 13(2), 85.
7 Gaballah, A., Parsa, V., Andreetta, M., & Adams, S. (2019). Objective and Subjective Speech Quality Assessment of Amplification Devices for Patients With Parkinson’s Disease. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, IEEE Transactions on, IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng, 27(6), 1226–1235. https://doi-org.proxy2.cl.msu.edu/10.1109/TNSRE.2019.2915172
8 Greene, M. C. L., Watson, B. W., Gay, P., & Townsend, D. B. K. (1972). A therapeutic speech amplifier and its use in speech therapy. The Journal of Laryngology & Otology, 86(6), 595-605–605. https://doi-org.proxy2.cl.msu.edu/10.1017/S0022215100075629
9 Knowles, T., Adams, S. G., Page, A., Cushnie-Sparrow, D., & Jog, M. (2020). A Comparison of Speech Amplification and Personal Communication Devices for Hypophonia. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 63(8), 2695–2712. https://doi-org.proxy2.cl.msu.edu/10.1044/2020_JSLHR-20-00085
10 Iddon, H., Read, J., & Miller, N. (2015). Does voice amplification increase intelligibility in people with Parkinson’s disease? International Journal of Therapy & Rehabilitation, 22(10), 479–486. https://doi-org.proxy2.cl.msu.edu/10.12968/ijtr.2015.22.10.479
11 Neel AT. (2009). Effects of loud and amplified speech on sentence and word intelligibility in Parkinson disease. Journal of Speech, Language & Hearing Research, 52(4), 1021–1033. https://doi-org.proxy2.cl.msu.edu/10.1044/1092-4388(2008/08-0119)
12 Badh G, Knowles T. Acoustic and perceptual impact of face masks on speech: A scoping review. PLoS One. 2023 Aug 25;18(8):e0285009. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0285009. PMID: 37624795; PMCID: PMC10456191
13 Cline, N., Knowles, T., & Badh, G. (2023). Effect of Face Masks and Speech Style on Speech Intelligibility and Listener Effort in Parkinson’s Disease. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 32(5), 2282–2296. https://doi-org.proxy1.cl.msu.edu/10.1044/2023_AJSLP-23-00085
14 Simantiraki, O., Cooke, M., & Pantazis, Y. (2020). Effects of Spectral Tilt on Listeners’ Preferences And Intelligibility. ICASSP 2020 - 2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), ICASSP 2020 - 2020 IEEE International Conference On, 6254–6258. https://doi-org.proxy2.cl.msu.edu/10.1109/ICASSP40776.2020.905411
15 Murton, O., Hillman, R., & Mehta, D. (2020). Cepstral Peak Prominence Values for Clinical Voice Evaluation. American journal of speech-language pathology, 29(3), 1596–1607. https://doi.org/10.1044/2020_AJSLP-20-00001