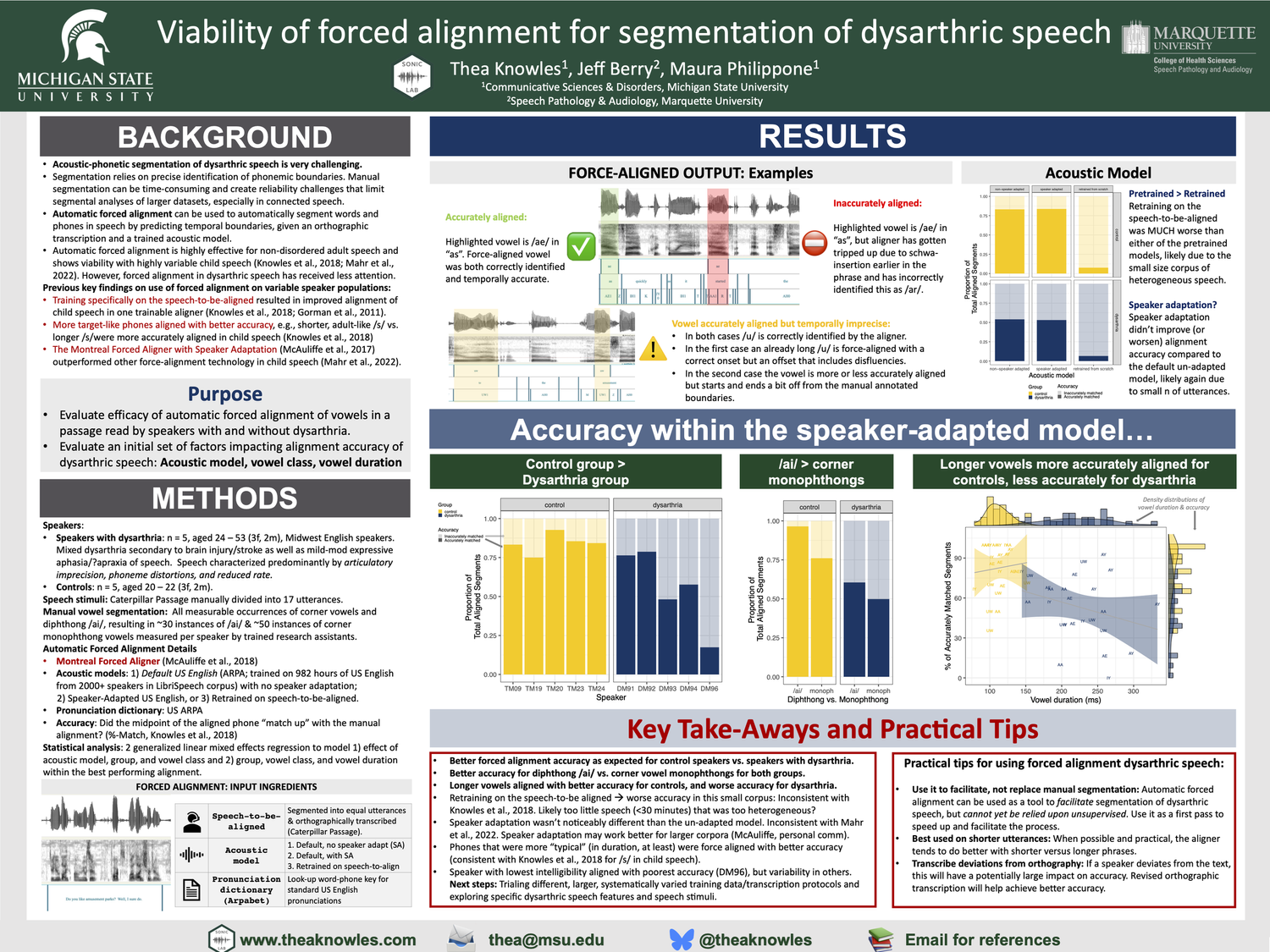
Viability of Forced Alignment for Segmentation of Dysarthric Speech
Thea Knowles, Jeff Berry, Maura Philippone
Presented at the Motor Speech Conference
San Diego, February 21, 2024
References
Gorman, K., Howell, J., & Wagner, M. (2011). Prosodylab-aligner: A tool for forced alignment of laboratory speech. Canadian Acoustics, 39(3), 192–193.
Knowles, T., Clayards, M., & Sonderegger, M. (2018). Examining factors influencing the viability of automatic acoustic analysis of child speech. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 61(10), 2487–2501. https://doi.org/10.1044/2018_JSLHR-S-17-0275
Mahr, T. J., Berisha, V., Kawabata, K., Liss, J., & Hustad, K. C. (2021). Performance of Forced-Alignment Algorithms on Children’s Speech. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research : JSLHR, 64(6 Suppl), 2213–2222. https://doi.org/10.1044/2020_JSLHR-20-00268
McAuliffe, M., Socolof, M., Mihuc, S., Wagner, M., & Sonderegger, M. (2017). Montreal Forced Aligner: Trainable text-speech alignment using Kaldi. Proceedings of Interspeech 2017, 498–502. https://doi.org/10.21437/interspeech.2017-1386
Patel, R., Connaghan, K., Franco, D., Edsall, E., Forgit, D., Olsen, L., Ramage, L., Tyler, E., & Russell, S. (2013). “The Caterpillar”: A Novel Reading Passage for Assessment of Motor Speech Disorders. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 22(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1044/1058-0360(2012/11-0134)